0
0
 0
0
rank #3 ·
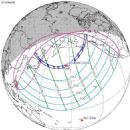
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit between Thursday, February 4 and Friday, February 5, 1943, with a magnitude of 1.0331. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 22 hours after perigee (on February 4, 1943, at 1:30 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.